Women's Health
Endocrine Hypertension: What You Need To Know

Endocrine hypertension refers to high blood pressure caused by issues with the endocrine system, usually by the adrenal or pituitary gland. The system is responsible for producing hormones in the body, which are responsible for many bodily functions like growth and blood pressure.
When measuring blood pressure, your healthcare provider typically looks for 2 measurements:
- Systolic blood pressure: Blood vessel pressure during a heart beat
- Diastolic blood pressure: Blood vessel pressure between heart beats
A normal blood pressure measurement is less than 120/80. Once your blood pressure rises above this measurement, you will be monitored for high blood pressure and it’s a condition that can be treated.
Health problems may arise if blood pressure remains high for a long time. When left untreated, it can lead to heart disease, stroke and kidney failure.
Read on to learn more about the types of endocrine hypertension, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
Types Of Endocrine Hypertension
There are several different types of endocrine hypertension. They are caused by hormonal imbalance, such as the underproduction or overproduction of hormones.
Primary Aldosteronism (Conn’s Syndrome)
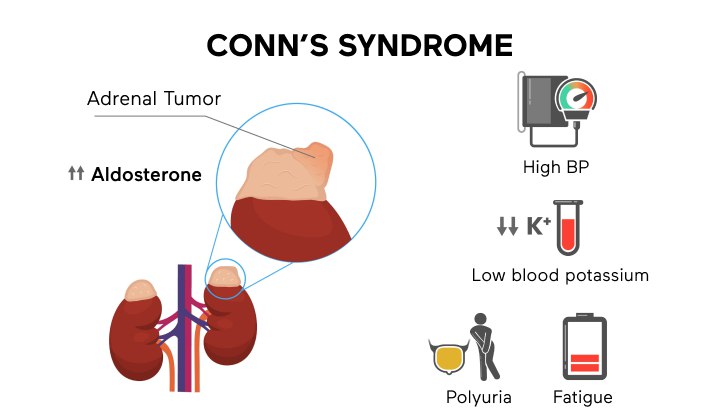
Also known as Conn’s syndrome, primary aldosteronism is the most common form of endocrine hypertension. This condition is caused by the overproduction of aldosterone, a hormone produced by the adrenal gland. Aldosterone is responsible for the retention of salt in your body and the overproduction of this hormone may cause excess salt and fluid levels.
Primary aldosteronism usually presents with high blood pressure and low potassium levels in the blood. When untreated, high blood pressure increases your risk for complications for heart attack and stroke, while low potassium can cause heart issues.
Cushing’s Syndrome (Hypercortisolism)
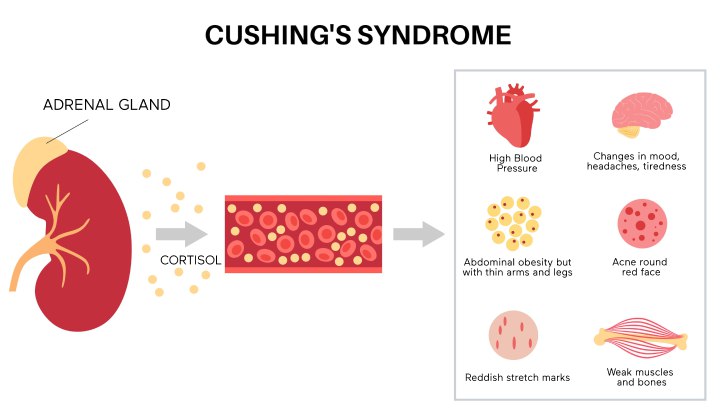
Cushing’s syndrome is a condition resulting from excessive cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands. The most common Cushing’s syndrome is Cushing’s disease, caused by excessive production of the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) by the pituitary gland. ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol.
Cushing’s syndrome can be caused by a tumour of the pituitary gland, a tumour of the adrenal gland, or by long-term use of corticosteroids.
Treatment for Cushing’s syndrome depends largely on its cause. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove the tumour or the pituitary or adrenal glands. Other treatment options may include radiation, chemotherapy, and hormone-inhibiting drugs.
Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare, usually non-cancerous (benign) tumour that develops in the adrenal gland. Usually, a pheochromocytoma develops in only one adrenal gland, although tumours can develop in both.
If you have a pheochromocytoma, the tumour releases hormones that may cause high blood pressure, headache, sweating and other health conditions. When it is left untreated, severe or other life-threatening damages to the body can occur.
Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a rare condition where the pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone, which can cause your body tissue and bones to grow extremely quickly.
When you have too much growth hormone, your bones increase in size. In childhood, this leads to increased height, however, in adulthood, changes in height doesn’t occur. Instead, increase in bone size is limited to the bones of your hands, feet and face, and is called acromegaly.
95% of these cases are caused by pituitary adenoma, a tumour in the gland. Symptoms include joint and muscle problems, headache and vision problems. Left untreated, it can lead to hypertension and diabetes.
Thyroid Problems: Hyperthyroidism or Hypothyroidism
When the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism) or produces too much thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism), it can result in high blood pressure.
Typically, hypothyroidism elevates the diastolic pressure more than the systolic pressure, whereas hyperthyroidism elevates the systolic pressure more than the diastolic pressure.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, feeling cold all the time, weight gain, constipation, hair loss and dry skin. On the other hand, symptoms of hyperthyroidism include feeling hot all the time, tremors, racing heartbeat and weight loss.
Lowering one’s blood pressure to normal is part of the treatment plan for those with thyroid disorders.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the disorder. For example, patients with Cushing’s syndrome might observe symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain and depression.
Some general symptoms are:
- Palpitations
- Headaches
- Profuse sweating
- Anxiety-like attacks
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness
Diagnosis
Endocrine hypertension can be hard to diagnose. To identify any abnormalities in hormonal levels, your endocrinologist would usually conduct a physical examination and examine your medical history. The following tests may also be administered to scan and identify any abnormalities in the hormones in the respective glands:
Blood Test
The hormone blood test measures the various hormone levels in the blood samples collected. Hormones measured may include metanephrines, thyroid, aldosterone, and cortisol hormone levels.
Urine Test
The hormone urine test would measure the various hormone levels in the urine. Hormones measured may include urine catecholamines and cortisol hormone levels.
Imaging tests
Imaging tests like MRI or CT scans may also be required to help visualize the glands and diagnose any visible issues.
Treatment
Endocrine hypertension is potentially curable if the underlying cause is identified and treated accordingly. If you find yourself with the above symptoms, seek medical treatment as soon as possible.
Lifestyle modifications
Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, eating a healthy diet and quitting smoking are essential to reduce blood pressure levels.
Medicine
Your specialist may prescribe medicine to decrease hormone production or replace your hormones. For example, for patients with conn’s syndrome, medicine that blocks the production of aldosterone may be used.
Surgery
Surgery may sometimes be necessary to remove a tumour or tissue that has been causing excessive production of a hormone.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy may also be administered to shrink the tumour and prevent further growth.
Conclusion
It is important to seek medical treatment if you have high blood pressure readings and are experiencing symptoms of endocrine hypertension. Endocrine hypertension needs to be excluded in most young patients who presents with high blood pressure. This is because endocrine hypertension has a positive outlook with accurate diagnosis and getting the right treatment. Depending on your health and medical conditions, your doctor may set a blood pressure goal and guide your treatment based on your risk factors. It is also important to monitor your blood pressure at home and bring your records to the doctor at each visit.
WHO WE ARE
About SOG Health Pte. Ltd.
Established in 2011, SOG Health Pte. Ltd. (“SOG”) is a leading healthcare service provider dedicated to delivering holistic health and wellness services to the modern family.
With a long and established track record in Singapore providing Obstetrics and Gynaecology (“O&G”) services such as pre-pregnancy counselling, delivery, pregnancy and post-delivery care, the Group has since further expanded its spectrum of healthcare services to include Paediatrics, Dermatology, and Cancer-related General Surgery (Colorectal, Breast & Thyroid).
The Group’s clinics, under its four operating segments of O&G, Paediatrics, Oncology and Dermatology, are strategically located throughout Singapore to provide easy access to its patients.
- Obstetrics
- Gynaecology
- GynaeOncology
- Breast, Thyroid & General Surgery
- Colorectal, Endoscopy & General Surgery
- Dermatology
- Paediatrics
Consult With A Specialist From SOG
Visit one of our specialists today to learn more about your health!
Recommended Specialists
Book An Appointment
Fill up this form and our clinic will get back to you shortly.
For general enquiries, please click here.