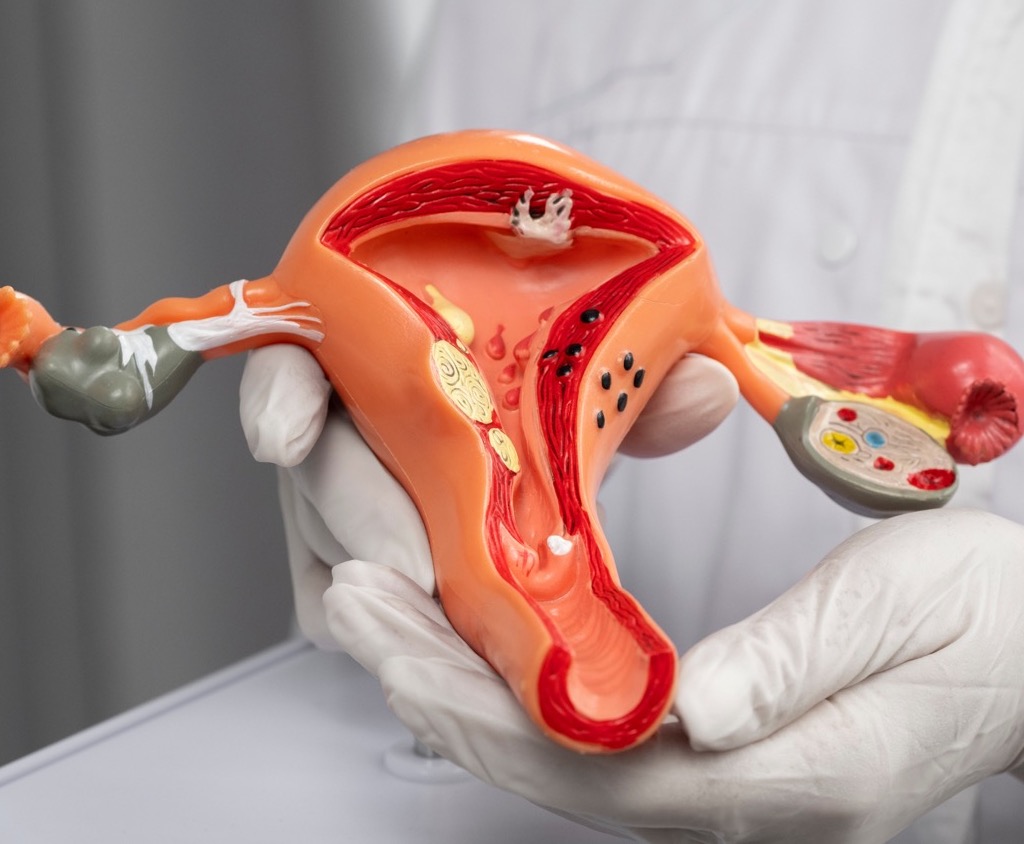
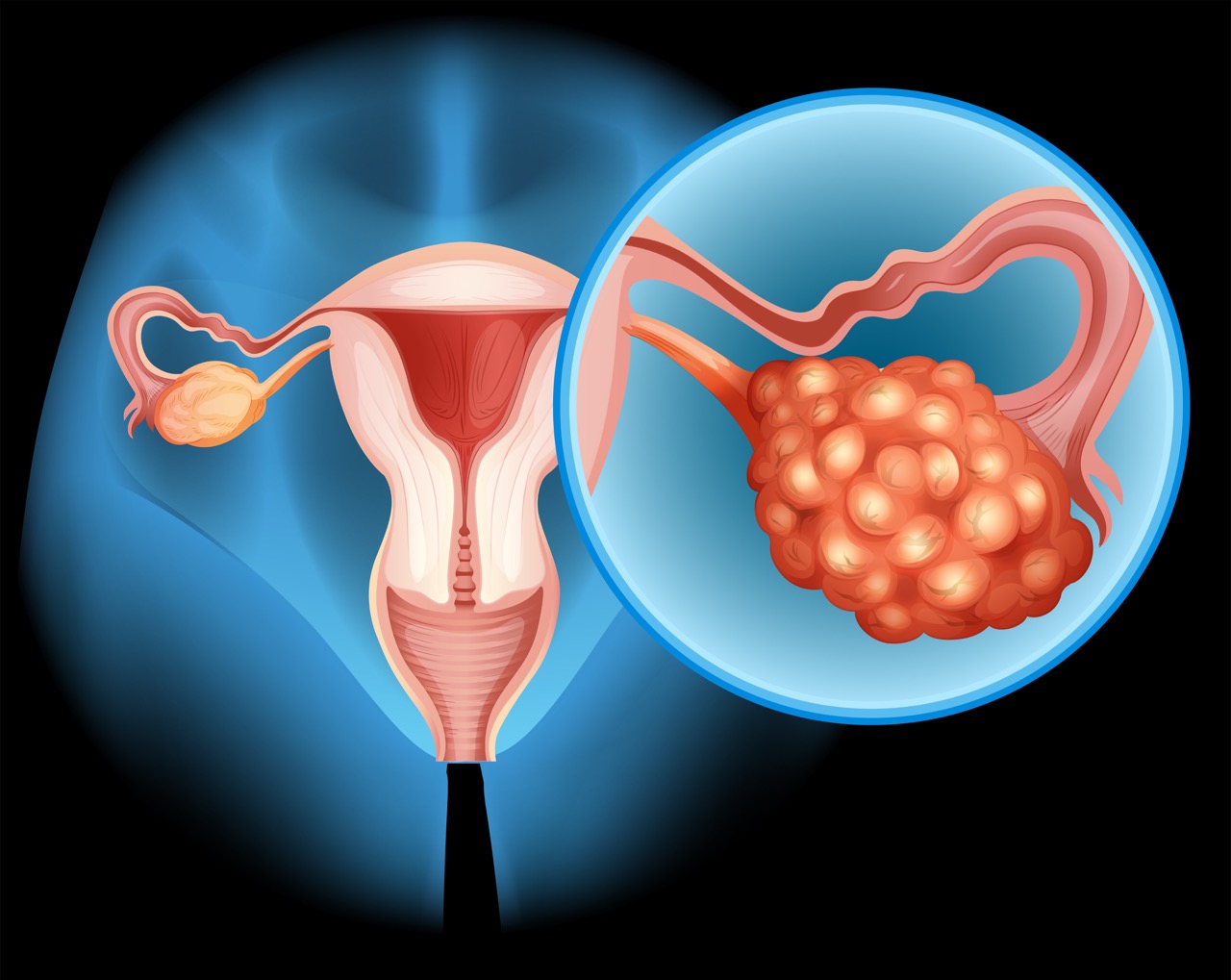
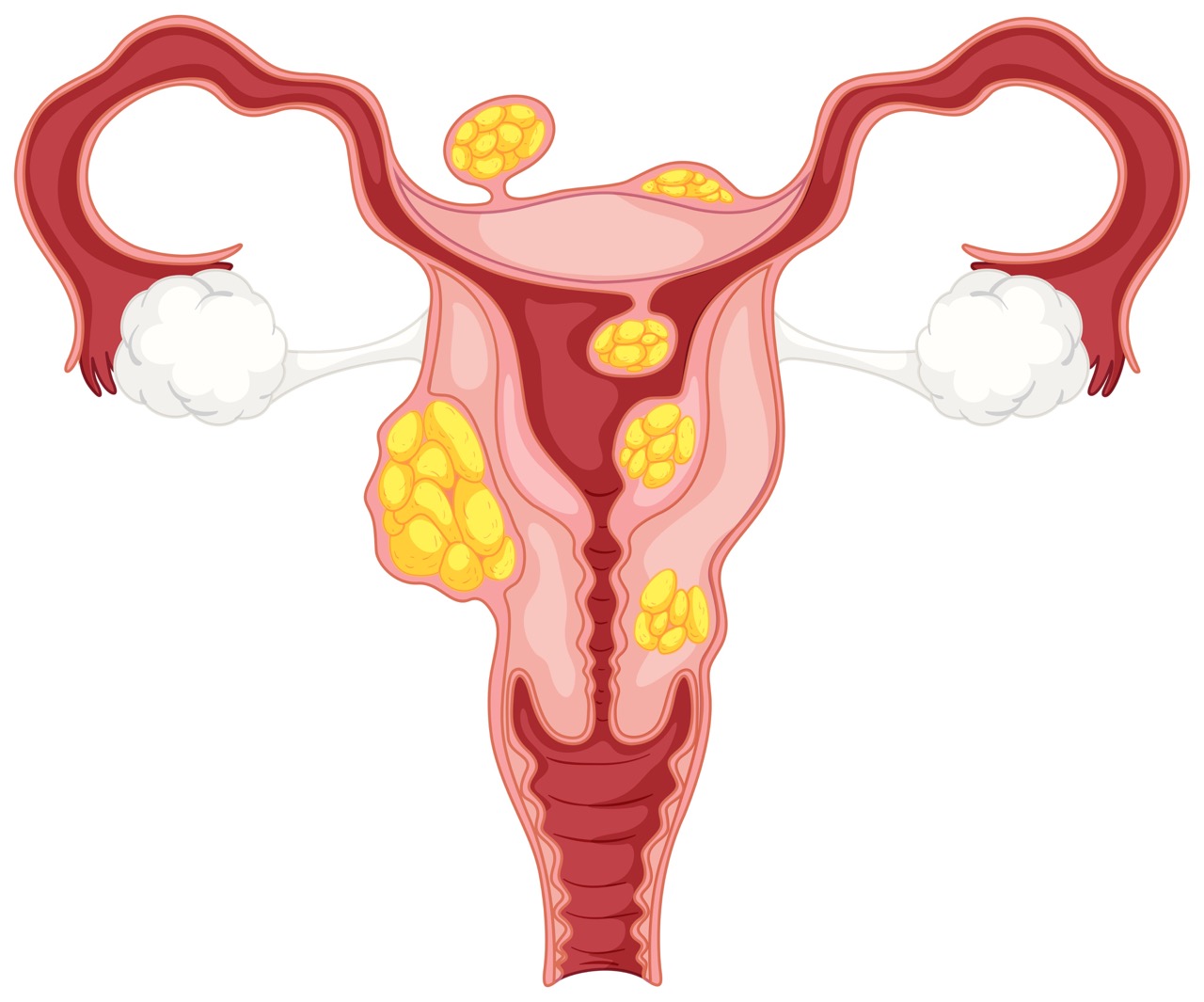
What Is An Ovarian Cyst?
A cyst simply means a collection of fluid. As most of the tumours formed in the ovary tend to contain fluid, it is commonly and popularly referred to as “ovarian cyst”.
How Many Types Of Ovarian Cysts Are There?
Fortunately, the non-cancerous types are most common, and they can be further classified according to its content and origin eg dermoid cyst (that may contain hairs, oils, bones, tooth etc), endometriotic or chocolate cyst, mucinous cyst etc. The cancerous form tends to occur in the extremes of age, prepubertal or adolescent, and the postmenopausal.
How Do I Know I Have Ovarian Cyst?
Some cysts, especially bigger ones, produce pain or pressure symptoms eg pressing on the bladder causing difficulty to hold your urine. The pain associated may be intermittent in nature, worsened during menses or occasionally, very severe and acute. The latter happens when the cyst ruptures or undergoes torsion. Torsion of the ovary is an emergency, not only it causes immense pain, but you may lose the entire ovary as the blood supply is disrupted.
It is not uncommon too to have “silent” cyst i.e. one that does not produce any symptoms, and is detected only at some routine gynaecological examination, or health screening. Ultrasound examination is by far the most important and useful tool for the detection of ovarian cyst.
How Can The Cyst Affect My Health?
The most important issues are the nature and size of the cyst. Cancerous growth is of course harmful, and urgent treatment is needed.
Non-cancerous cyst tends to cause pain or discomfort when it reaches certain size. If it grows too big, the remaining healthy ovarian tissue may be destroyed. Some non-cancerous cyst may also affect the menses or fertility potential by interfering with ovarian function.
What is the treatment available?
Not all cysts need to be removed. Some of the smaller cysts are simply physiological and will disappear over 6 8 weeks. Some of the cysts are however pathological and will not disappear but tend to grow with time.
The most important thing is to exclude cancer. A detailed medical history, examination, ultrasound and sometimes blood tests are important preliminary steps. Depending on the information gathered, surgery or just monitoring of the cyst may be recommended.
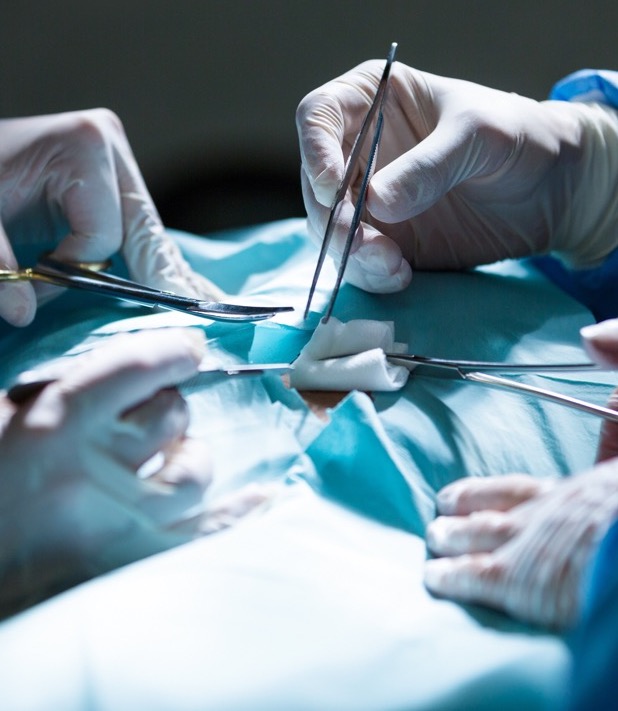
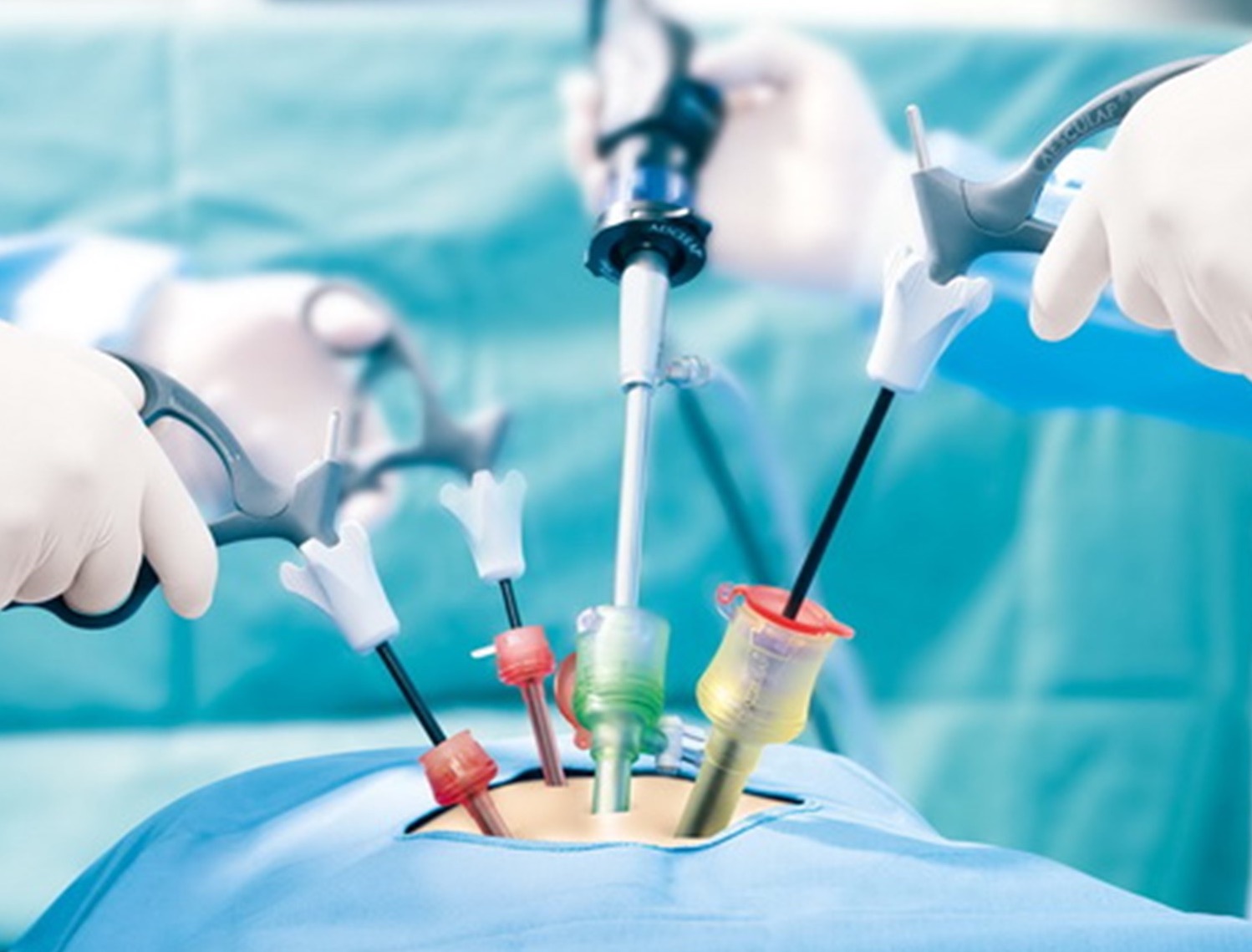
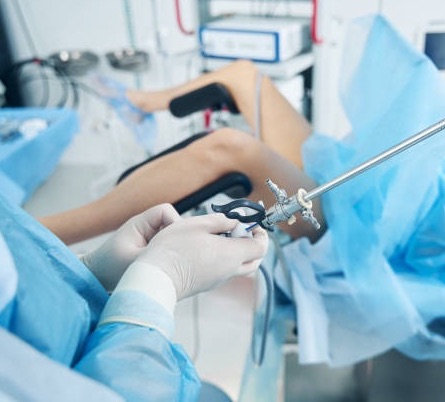
What Kind Of Surgery Is Available?
Presently, video-laparoscopic (or keyhole) surgery is the method of choice for removing most non-cancerous cyst. If cancerous growth is strongly suspected, a laparotomy is then necessary, unless the cancer is still in early stage.